- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming
In computer programming, how do I check if two Strings are Anagrams?
What are strings?
In most programming languages, a string is simply an array of individual characters. This is common among all languages that support strings. The actual implementation differs between languages.
Some programming languages allow characters to be changed inside the string, while others do not. When a string can have its characters edited, it is called "mutable." When a string cannot have its characters edited, it is called "immutable." C++ allows the individual characters of a string to be edited, so it is mutable. C# does not allow the individual characters of a string to be edited, so it is immutable. Any edits to a string in C# results in the program allocating enough memory for the new string, and then creating the new string in that place.
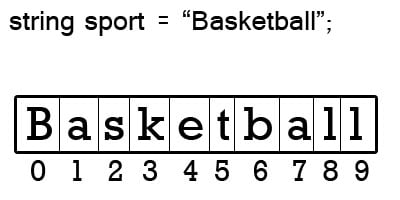
Another thing to be aware of with your programming language of choice is how the environment indexes collections. Both C++ and C# will refer to the very first character as being in position 0. If a string had 10 characters, such as "Basketball", then the first character would be in position 0 and the final character in position 9. This is called "zero-based indexing." Other languages will refer to the first character as position 1, and the final character as position 10. This is called "one-based indexing." Visual Basic uses one-based indexing by default, but can be set to use zero-based indexing. SmallTalk and Lua both use one-based indexing as well.
What is an anagram?
An anagram is simply two different words that both use the same number of each letter. For example, the words "Aether" and "Heater" are anagrams. Both contain one letter "A", two letters "E", one letter "H", one letter "R", and one letter "T." Notice how there is no distinction between uppercase and lowercase letters here.
Anagrams are easy to spot within the English language, but in order to establish a definition in a computer program, we are going to set some rules about the definition of an anagram.
1. Two words that are the same are not considered an anagram.
2. There is no distinction between uppercase and lowercase letter characters.
3. Strings that contain characters other than letters will not be considered. Sorry, contractions.
Checking if two strings are anagrams
There are a number of different ways to check if two strings are an anagram.
The first way is to use nested loops to make sure each character appearing in the first string also appears in the second. I don't recommend this method, because it results in a solution that is O(N ^ 2) time.
The second way is to sort both strings, then compare each character. I don't recommend this method for two reasons.
- Sorting the strings will take O(N log(N)) time on average if QuickSort or MergeSort are implemented.
- Some languages will have immutable strings, making sorting difficult.
The final implementation is to iterate over each string once, counting the number of each character as you do so. After iterating over each string, make sure the counts of all characters are the same. This is my preferred method since it is done in O(N) time.
Anagram Implementation: C++
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <ctype.h>
using namespace std;
bool CheckAlphaOnly(string str)
{
//Check if each character of a given string is alphabetic.
//If any character fails, then return false.
//Otherwise, return true.
for (uint x = 0; x < str.length(); x++)
{
if (isalpha(str[x]) == false)
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool IsAnagram(string str1, string str2)
{
//Check if two strings are anagrams.
//If strings are not equal length, return false.
if (str1.length() != str2.length())
return false;
//Arrays to count the number of each alphabetic character.
int arr1[26] = { }, arr2[26] = { };
int index;
//Count characters for str1.
for (uint x = 0; x < str1.length(); x++)
{
index = (int)toupper(str1[x]) - (int)'A';
arr1[index]++;
}
//Count characters for str2.
for (uint x = 0; x < str2.length(); x++)
{
index = (int)toupper(str2[x]) - (int)'A';
arr2[index]++;
}
//Check to see if the count for each character is the same.
//If any character check fails, return false.
//Otherwise, return true.
for (int x = 0; x < 26; x++)
{
if (arr1[x] != arr2[x])
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
cout << "Please enter two strings.\n";
cout << "Alphabetic characters only.\n\n";
string str1 = "", str2 = "";
cout << "String 1: ";
getline(cin, str1);
cout << "\nString 2: ";
getline(cin, str2);
if (CheckAlphaOnly(str1) && CheckAlphaOnly(str2))
{
if (str1 == str2)
cout << "\nThese strings are the same.";
else if (IsAnagram(str1, str2))
cout << "\nThese strings are anagrams.";
else
cout << "\nThese strings are not anagrams.";
return 0;
}
else
{
cout << "\nError: One or both strings contained non-alphabetic characters.";
return -1;
}
}Anagram Implementation: C#
using System;
namespace Anagrams
{
class Program
{
static bool CheckAlphaOnly(string str)
{
//Check if each character of a given string is alphabetic.
//If any character fails, then return false.
//Otherwise, return true.
for (int x = 0; x < str.Length; x++)
{
if (Char.IsLetter(str[x]) == false)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static bool IsAnagram(string str1, string str2)
{
//Check if two strings are anagrams.
//If strings are not equal length, return false.
if (str1.Length != str2.Length)
return false;
//Arrays to count the number of each alphabetic character.
int[] arr1 = new int[26], arr2 = new int [26];
//Initialize the arrays.
for (int x = 0; x < 26; x ++)
{
arr1[x] = 0;
arr2[x] = 0;
}
int index;
//Count characters for str1.
for (int x = 0; x < str1.Length; x++)
{
index = (int)Char.ToUpper(str1[x]) - (int)'A';
arr1[index]++;
}
//Count characters for str2.
for (int x = 0; x < str2.Length; x++)
{
index = (int)Char.ToUpper(str2[x]) - (int)'A';
arr2[index]++;
}
//Check to see if the count for each character is the same.
//If any character check fails, return false.
//Otherwise, return true.
for (int x = 0; x < 26; x++)
{
if (arr1[x] != arr2[x])
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Please enter two strings.");
Console.WriteLine("Alphabetic characters only.\n");
string str1 = "", str2 = "";
Console.Write("String 1: ");
str1 = Console.ReadLine();
Console.Write("\nString 2: ");
str2 = Console.ReadLine();
if (CheckAlphaOnly(str1) && CheckAlphaOnly(str2))
{
if (str1 == str2)
Console.WriteLine("\nThese strings are the same.");
else if (IsAnagram(str1, str2))
Console.WriteLine("\nThese strings are anagrams.");
else
Console.WriteLine("\nThese strings are not anagrams.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("\nError: One or both strings contained non-alphabetic characters.");
}
Console.WriteLine("\nPlease press [ENTER] to exit...");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}





